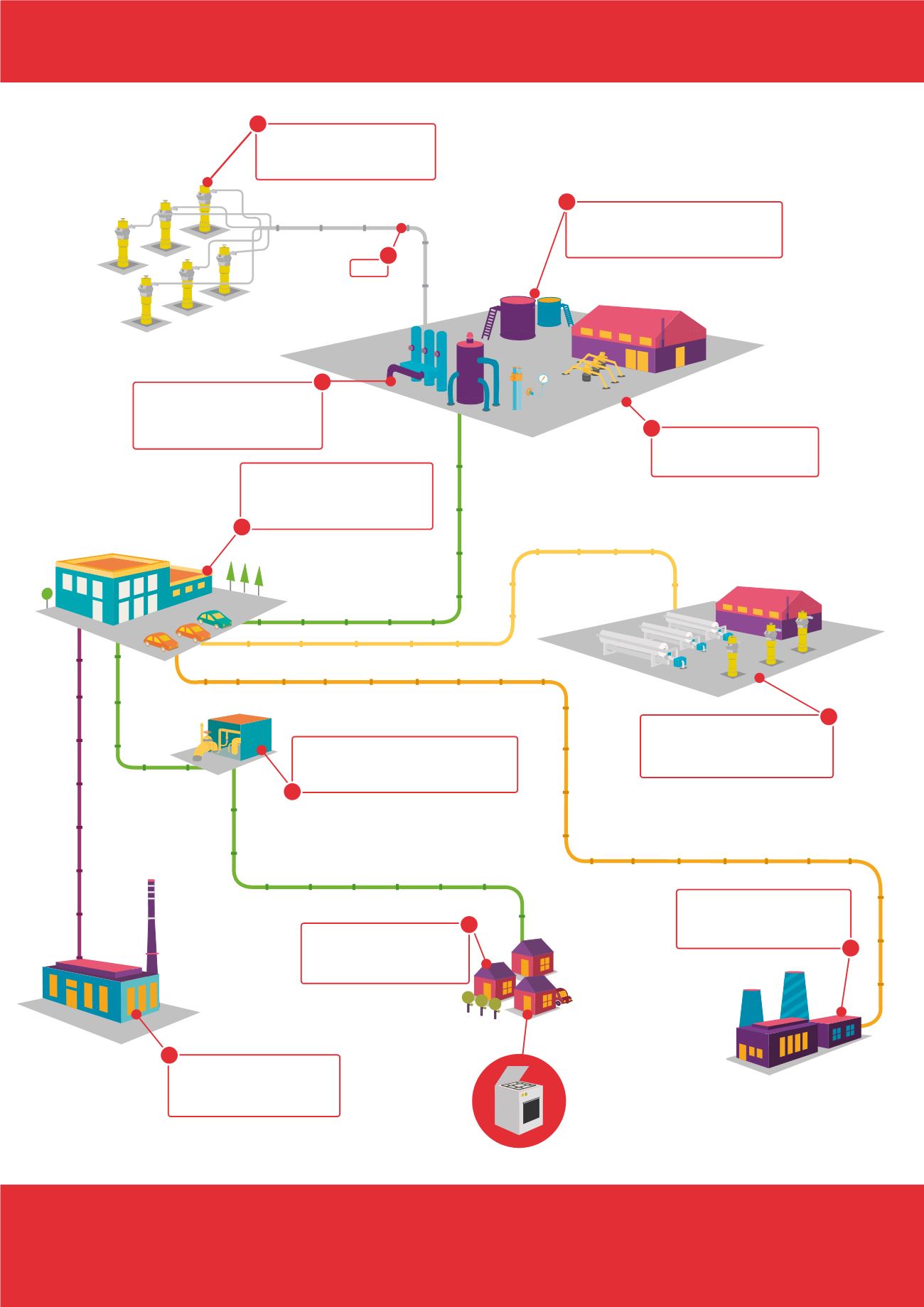
1
transmission pipeline
gathering pipeline system
transmission pipeline
distribution pipeline
Gas processing plant
Industrial plants
Gas used in mass production
(e.g., in chemical plants or
nitrate plants).
Households
Individual consumers of gas,
which used in gas cookers or
to heat houses.
Gas storage
Underground storage
(in natural geological formations)
or surface storage (in gas tanks).
Pressure reduction and monitoring station
Adjusts the pressure and controls
the quantity of gas flowing through.
Gas transmission and distribution
system operators
Manage the transmission
and distribution of gas.
Compressor station
To compress gas and adjust
its flow and pressure.
Wastewater storage
Tanks used to collect water separated from
gas during the process of dehydration.
Gas treatment instalation
Dehydration of gas, removal
of CO
2
, H
2
S, sulfur, mercury
and heavy hydrocarbons.
Wellhead/ Christmas tree
Seals the surface end
of the production well.
Pipes
District heating plants
Use gas to heat water,
which is necessary for district
heating networks.
PRODUCTION, DISTRIBUTION AND USE OF NATURAL GAS
THE DIAGRAM SHOWS THE ROUTE GAS TAKES FROM BEING BROUGHT TO THE SURFACE TO FINDING ITS WAY TO THE END USER (E.G., A DETACHED
HOUSE OR A DISTRICT HEATING PLANT). NATURAL GAS, AS EXTRACTED FROM A BOREHOLE, DIFFERS SIGNIFICANTLY FROM THE GAS USED IN OVENS
OR BOILERS. ITS PROPERTIES CHANGE, MAINLY DURING ITS PROCESSING IN A GAS PROCESSING PLANT, WHERE IT IS DEHYDRATED, PURIFIED AND
ODORIZED. THEN IT IS PRESSURISED AND TRANSPORTED BY PIPELINE TO STORAGE, INDUSTRIAL PLANTS, OR HOUSEHOLDS. THE TRANSMISSION OF
GAS IS MANAGED BY SPECIALISED COMPANIES AND INSTITUTIONS KNOWN AS TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION NETWORK OPERATORS.


